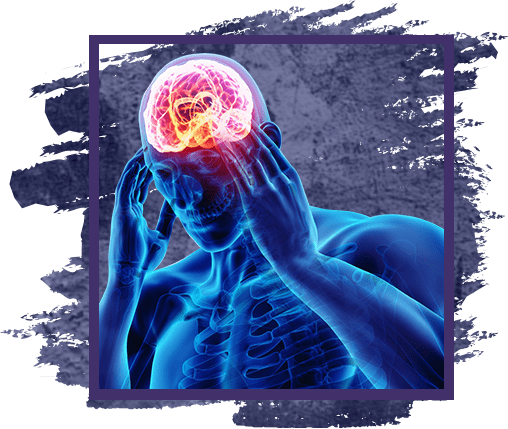
Migraine is a disease characterized by episodic paroxysmal headaches of considerable intensity, which are usually accompanied by nausea and / or hypersensitivity to light and sounds. Migraine is also characterized, but not necessarily, by increased pain during exertion and walking, pulsating, one-sided or predominance on one side. Characterized by a decrease in working capacity, performance, up to complete loss during an attack. Decreased quality of life with frequent attacks.
This disease can significantly impair the quality of life, lead to a temporary decrease or temporary disability for a certain period of time. Therefore, it is important to carry out proper treatment, adequate relief of attacks and prevention of migraine attacks, both medicinal and behavioral, by following lifestyle recommendations, to avoid risk factors, provoking factors, so-called "triggers" of migraine. Diagnosis of migraine is mainly based on the collection of complaints and anamnesis, a description of the characteristics of attacks, details and the nature of the pain, all the details are important and a detailed conversation is required at the initial reception.
In some cases, neuroimaging methods are used to exclude other diseases masquerading as migraines - MRI, CT. Less commonly, blood tests, EEG, cardiological examination, ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head, lumbar puncture with cerebrospinal fluid analysis may be required.
Varieties of headache
Among patients seeking medical help with headache, primary forms of headache predominate (90-95%): migraine and tension headache. Rarer forms of primary headache are cluster headaches associated with physical exertion, cough, sexual activity, etc.
Tension headache - bilateral, squeezing "like a hoop, helmet", not pulsating, monotonous. Secondary headaches are symptomatic in relation to the underlying disease (organic lesions of the brain, face, neck, systemic diseases, neuralgia, facial pain), are much less common (5-10%).
Migraine is one of the most common reasons for going to a neurologist in everyday medical practice. According to statistics, up to 12% of the world's population suffers from this type of headache. Women are somewhat more likely to get sick. Most often, people suffering from migraine go to the doctor in connection with intense attacks that significantly impair the quality of life, at the age of 30-40 years. There is a genetic predisposition to this disease: if one of the closest relatives has a migraine, the risk of seizures is higher.
What causes migraines
According to modern concepts, the mechanism of a migraine attack is based on dysfunction of pain centers in the stem structures of the brain, depression of the bioelectrical activity of the cerebral cortex, excitation of the trigeminal nerve system, which leads to the release of local vascular inflammatory neurotransmitters, changes in vascular tone in the arteries and veins of the dura mater, neurogenic inflammation and edema of the vascular wall and extravascular space.
The main role in the understanding of the mechanisms of migraine is given to dysfunction of the trigeminal nerve system.
Neurotransmitters that play a significant role in the mechanism of migraine:
- Serotonin: the role is not fully understood, but the activation of serotonin receptors is used to stop seizures (drugs of the triptan group), and serotonin reuptake inhibitors that increase its concentration (antidepressants) can reduce the frequency of attacks.
- Calcitonin-gene related peptide (CGRP): the most promising neurotransmitter to date in the treatment of frequent attacks. Antibodies to this mediator are the most modern and promising group of drugs for the prevention of migraine attacks. During an attack, an increase in the level of CGRP in the venous blood and in the cerebrospinal fluid is detected. CGRP is secreted by neurons of the trigeminal nerve system and triggers the processes of neurogenic inflammation and edema in the vessels and surrounding tissues.
What provokes a migraine attack:
- Irregular meals during the day, hunger
- Alcohol (especially red wine)
- Stressful emotional situations
- Lack or excess of sleep, change in sleep patterns
- Some foods: nuts, hard cheeses, chocolate, foods containing glutamate, nitrite, aspartame, fats
- Smoking
- Weather changes
- Premenstrual syndrome
- Neck pain, spasm of the muscles of the neck and shoulder girdle
- Bright light, flickering light
- Heat
- Excessive physical activity
- Sexual activity
- Unpleasant odor
- Pathology of the temporomandibular joint
Symptoms of migraine
- Prodromal period: some patients feel a stereotypical change in well-being that precedes an attack. These can be emotional and psychological changes or autonomic symptoms. Most often describe a change in mood - euphoria, depression, depression, irritability; neck pain, neck stiffness; yawning, drowsiness; change in appetite. These symptoms can occur 24 to 48 hours before a migraine attack.
- 25% describe a migraine aura before or during a headache attack. Migraine with aura was previously called "classic migraine". Aura is a symptom of migraine, reflecting a depression of bioelectrical activity in the cerebral cortex. Depending on the area of the cortex where there is a violation of bioelectrical activity, there are certain focal neurological symptoms: impaired vision, sensitivity, hearing. The aura can be positive (flashes in the eyes, tinnitus) and negative (loss of vision, hearing, numbness).The usual duration of the aura is 30-60 minutes. Sometimes longer. Most often, the aura precedes a migraine headache. With the completion of the aura, a headache begins. According to the latest data, often the aura accompanies the headache in parallel. The most common aura is visual. Blurred in the field of view, zigzags, "lightning", silver or golden, gradually increases, lasting up to 1 hour. Less often - sensory aura (numbness of the face, limbs), motor aura (involuntary movements). Vestibular aura in the form of rotational vertigo. There is a form of migraine in the form of an aura without a headache, that is, there are attacks of an isolated aura.
- Headache is the main symptom of migraine. It occurs after the prodromal period and aura (if any).
- Postdromal (post-attack period) - after an intense migraine attack, some patients note fatigue, absent-mindedness, weakness for hours or days, soreness occurs during sudden movements in the area of the head where there was migraine pain, a feeling of "empty head".
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of migraine is mainly based on the typical manifestations of the disease, identified in the study of complaints and the patient's history. The diagnosis is clinical, requires a detailed collection of complaints, anamnesis, and a neurological examination of the patient.
The diagnosis of "migraine" is more likely with symptoms associated with headaches, such as nausea, phono and photophobia, limitation of physical activity.
According to the International Classification of Headaches 3rd edition (ICHD-3), there are clear criteria (especially a patient's headache), when a certain combination of which is detected, a diagnosis of migraine is established.
Neuroimaging (MRI, CT) is not necessary in all cases. According to international recommendations, it is necessary to conduct these studies in case of suspicion of the secondary nature of pain, the conditionality of a headache by another disease, as well as in the detection of violations during examination in the neurological status, with atypical manifestations, symptoms, features.
Forms of migraine
Episodic - less than 15 attacks per month. Often 1-2 attacks or 1 attack in a few months.
Chronic - more than 15 attacks per month for 3 months over the past year.
It is established reliably when keeping a headache diary.
Treatment of migraine
Migraine treatment includes:- Treatment of a migraine attack
- Preventive treatment aimed at preventing seizures, with frequent attacks
Treatment of a migraine attack
The drug should be taken as early as possible: at the beginning of the aura or at the onset of a headache.
- Analgesics (painkillers) - aspirin, paracetamol, ibuprofen, naproxen, indomethacin. In the case of moderate pain, caffeine can help. Analgesics should not be taken too often, no more than 8-10 tablets per month, otherwise addiction may occur, as a result of which the so-called abusive (drug-conditioned) headaches develop.
- With the ineffectiveness of analgesics, triptans (sumatriptan, eletriptan, etc.), specialized drugs for the treatment of migraine are prescribed. Activate serotonin receptors, are able to interrupt the pathological mechanism of the development of a migraine attack. There is a risk of side effects and restrictions, contraindicated in pregnancy, in serious diseases of the cardiovascular system. Triptans exist in the form of tablets, capsules, in the form of a nasal spray (which facilitates the administration of the drug in case of severe nausea). A specific drug is selected individually. More than 8-9 doses per month - the risk of addiction, the development of drug-induced headaches (abuse).
- For nausea, vomiting, antiemetic drugs are used, such as metoclopramide in tablet or injection form.

Prevention of migraine
With ineffective treatment of seizures or the constant presence of factors that provoke migraine, it is possible to increase the frequency of attacks and their intensity, up to the transition to the form of chronic migraine, which can lead to a significant decrease in the quality of life, restrictions on daily activity, a decrease or temporary disability.
In this case, prophylactic migraine therapy (preventive) is carried out, aimed at routine medication in order to prevent attacks. A number of groups of drugs are used. It is equally important to follow lifestyle recommendations, avoid risk factors and "triggers".
Beta-blockers: drugs from cardiology, to reduce pressure and treat tachycardia. Indicators in a number of patients are effective in the form of migraine prevention. Metoprolol, anaprillin are commonly used.
- Antidepressants (amitriptyline, etc.). May cause drowsiness, usually prescribed at night. Modern drugs have a lower risk of adverse reactions. By increasing the concentration of serotonin in the nervous tissue, they reduce the risk of pathological mechanisms leading to a migraine attack.
- Anticonvulsants (antiepileptic drugs). In anticonvulsants Topiramate and Valproate, an anti-migraine effect was revealed. Often used to prevent seizures when the course worsens. May cause drowsiness, loss of appetite, decreased concentration.
- The course of treatment with prophylactic therapy usually requires at least 3 months and can be extended according to clinical need. Prophylactic therapy for migraine is also used for an overdose of analgesics and the occurrence of drug-induced headaches.
- Botulinum toxin type A. The drug is used to treat chronic migraine when it is combined with symptoms of neck pain, spasm of the neck muscles. It shows good efficacy, in Russia it has been used since 2011 for the treatment of migraine. In the United States since the early 2000s. Injections of small doses of the drug are carried out in the most often painful points in the muscles of the head, neck, shoulder girdle, where there are zones associated with the systemic trigeminal nerve and exciting the trigeminal nerve with muscle spasm in these areas.
- Calcitonin-related peptide gene (CGRP) antagonists, the most promising and novel group of drugs. Artificially synthesized antibodies to CGRP molecules or receptors of this neurotransmitter. They are used in the form of subcutaneous injections 1 time per month. Several drugs have been registered in the United States since 2018 and are actively used in clinical practice, showing good efficacy. There are no side effects characteristic of antidepressants and anticonvulsants. In the Russian Federation, in the process of registration, they may appear in 2020.
Physiotherapy treatment
When combining migraine with neck pain, hypertonicity and spasm of the muscles of the scalp, neck, shoulder girdle, physiotherapists are involved. Often the appearance of spasm in the muscles of the neck, in the trapezius muscles are a trigger for migraine and trigger an attack. Prevention of muscle spasm in this case is the prevention of migraine.
Apply for hypertonicity physiotherapy, gentle massage, muscle techniques of manual therapy, acupuncture, apparatus physiotherapy.
Prevention of muscle-tonic phenomena in this area - regular gymnastics, swimming.
There is evidence of the effectiveness of external electrical stimulation of the trigeminal nerve projection zones in the head and neck. There are hoops on the market for treatment during the day.
Psychotherapeutic treatment
With significant stress, psycho-emotional instability, depression, the involvement of a psychiatrist, psychotherapist is required. Depression and anxiety disorders provoke and exacerbate migraines. Techniques of psychotherapy, auto-training, meditation, relaxation training are used. Migraine Prevention Behaviors, Lifestyle Recommendations.
It is desirable to limit the influence of factors that can provoke a migraine attack:
- irregular meals during the day, hunger;
- alcohol (especially red wine);
- stressful emotional situations;
- lack or excess of sleep, change in the usual sleep pattern;
- some foods: nuts, hard cheeses, chocolate, foods containing glutamate, nitrites, aspartame;
- smoking.
- Regular moderate exercise (aerobic exercise, cardio training - walking on a treadmill at a fast pace, exercise bike, swimming, fitness) at least 1-2 times a week;
- Normalization of sleep and rest: falling asleep and waking up at the same time on weekdays and weekends, relaxing activities before bedtime;
- Normalization of diet: do not skip meals, it is useful to keep a food diary to identify provoking foods;
- If possible, avoid such provoking factors as bright intermittent light, excessively loud sounds;
- Keeping a "headache diary" to assess the course of migraine at long time intervals - on paper or in a smartphone application, this data is very important for the attending physician;
- Stress control: relaxation activities, if necessary, consultation with a psychotherapist to correct stressful influences;
- With frequent tension, spasm of the muscles of the neck, shoulder girdle, shoulder blades - measures to reduce spasm (physical education, swimming, massage).
Tips for behavior during a migraine attack:
- Taking the drugs prescribed for the relief of an attack as early as possible, in the first minutes of the attack or aura (as prescribed by the attending neurologist);
- Reduce light, loud sounds;
- Avoid physical activity;
- Try temperature treatment: a cold compress on the neck or head area can reduce pain, a warm compress or a warm shower can relax tense neck muscles;
- Try drinking a caffeinated drink at the beginning of an attack, but be careful - excess caffeine can also provoke migraines.
Complications of migraine
An attack that does not stop for 72 hours or more is called migraine status. It may require hospitalization in a hospital for adequate anesthesia, selection of therapy for relief and prevention of seizures in the future.
There may be cases of persistent aura without migraine. There is a perception that some forms of migraine can lead to stroke. This is an extremely rare occurrence. There is no consensus on whether these strokes are a complication of migraine or a case of stroke in a patient with migraine for another reason. In rare cases, migraines can lead to epilepsy.
 DE
DE FR
FR IT
IT ES
ES